Types of Vegetable Seeds: A Gardener’s Guide to Success
Published: 3 Dec 2024
Hello, gardening friends!
Have you ever considered why certain vegetables grow effortlessly in your garden while others struggle? The secret often lies in choosing the suitable types of vegetable seeds. Like a mechanic wouldn’t use a hammer to fix a watch, gardeners must select the right seeds for optimal plant growth.
Sheila, a botanist with seven years of experience, will use relatable analogies to guide you. In this article, we’ll explore the significant types of vegetable seeds, their characteristics, pros and cons, common mistakes in vegetable seed selection, essential factors, and a helpful FAQ section.
By the end, you’ll know which varieties of vegetable seeds will work best in your garden and how to achieve a fruitful harvest. Ready to begin?
A garden is a grand teacher. 🌱 It teaches patience and careful watchfulness; 👀 it teaches industry and thrift; 💪🌾 above all, it teaches entire trust. 🌻🤲 Gertrude Jekyll
Types of Vegetable Seeds
Selecting the appropriate type for your requirements is essential, as each has distinctive characteristics, advantages, and challenges. To help you in making an informed decision, we divide seeds and vegetables into four categories:
- Heirloom Vegetable Seeds
- Hybrid Vegetable Seeds
- Open-Pollinated Vegetable Seeds
- GMO Vegetable Seeds
1. Heirloom Vegetable Seeds
Heirloom vegetable seeds are open-pollinated and preserved for over 50 years. In my experience, they are ideal for gardeners who value biodiversity and sustainability. They also produce superior-quality vegetables.
Characteristics
- They are open-pollinated seeds
- They show unique shapes and flavours.
- They play a role in the preservation of biodiversity.

Advantages of Heirloom Seeds
- Better taste and flavour.
- Ability to save seeds for future planting.
Disadvantages of Heirloom Seeds
- Less disease resistance compared to hybrids.
Examples:
- Brandywine Tomato
- Black Beauty Eggplant
2. Hybrid Vegetable Seeds
In my experience, hybrid vegetable seedlings provide excellent disease resistance and yield. Their uniform growth makes them ideal for achieving consistent results.
Characteristics
- They provide uniform growth and appearance.
- They have enhanced resistance to diseases and pests.

Benefits of Hybrid Vegetable Seeds
- Higher yield and better adaptability.
- Improved vigor and consistency.
Limitations of Hybrid Vegetable Seeds
- Seeds are unsuitable for storage for the future season, as they will yield different results.
Examples
- Sugar Snap Peas
- Super Sweet 100 Cherry Tomato
3. Open-Pollinated Vegetable Seeds
Open-pollinated seeds reproduce naturally, maintain genetic stability, and can be saved for replanting. However, they may cross-pollinate and lack uniformity.
Characteristics
- They grow uniformly with a consistent appearance.
- They offer improved resistance to diseases and pests.

Advantages of Open-Pollinated Seeds
- Genetic stability.
- Ability to adapt to local growing conditions.
Disadvantages of Open-Pollinated Seeds
- Potential for cross-pollination with nearby plants.
Examples
- Straight Eight Cucumber
- Danvers Half-Long Carrot
- Detroit Dark Red Beet
4. GMO Vegetable Seeds
Genetically modified (GMO) vegetable seedlings are developed in laboratories to address characteristics such as pest resistance. They enhance yields; however, due to moral issues, they are unsuitable for replanting.
Characteristics
- GMO seeds are not usually available to home gardeners.
- They are primarily used in commercial agriculture.

Examples:
- Bt Corn (primarily commercial use)
- Roundup Ready Soybeans (commercially principally used)
| Controversies About GMO Seeds |
|---|
1. Environmental Concerns The controversies surrounding GMO vegetable seeds centre ethical, environmental, and legal issues. Critics argue that genetic modifications may harm biodiversity and disrupt natural ecosystems, posing risks to long-term environmental health. 2. Ethical and Legal Issues Additionally, ethical concerns arise from corporate control over seeds, limiting farmers’ independence. Patent laws prevent saving and replanting these seeds, increasing dependency on manufacturers and raising costs for growers, fueling debates on food security and fairness. 🚫💰 |
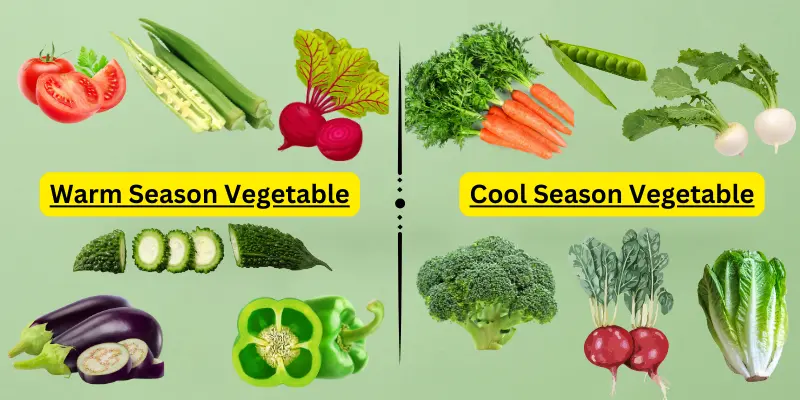
Seasonality: Cool-Season vs. Warm-Season Seeds
| Season | Suitable Vegetable Seeds | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Cool-season | Grow well in cooler Temperature | Lettuce, Peas, Broccoli, Spinach |
| warm-season | Thrive in warmer weather | Tomatoes, Cucumbers, Peppers |
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting Vegetable Seeds
You can choose seeds keeping in mind the below-mentioned suggestions.
- Purchase only the seeds you need.
- Consider your local climate and soil before buying.
- Research plant spacing and growth requirements in advance.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Vegetable Seeds
Choosing the right vegetable seeds depends on climate, soil, and space. Considering these factors ensures a successful harvest.
He who plants a garden plants happiness.🌱😊Chinese Proverb
1. Garden Layout and Space
- Determine how much space you have.
- Choose seeds that match your garden size and layout (e.g., bush vs. vine plants).
2. Climate and Growing Season
- Understand your local climate and hardiness zone.
- Select seeds suited to your growing season (cool-season vs. warm-season crops).
3. Soil and Water Requirements
- Evaluate your soil type and its drainage capabilities.
- Choose seeds with compatible water needs to avoid under or overwatering.
4. Disease and Pest Resistance 🐛
- Research common pests and diseases in your area.
- Choose varieties known for their resistance to these threats to reduce maintenance.
| Do You know? |
|---|
|
Final Words ✍️
Choosing the appropriate types of vegetable seeds is crucial to cultivating a thriving garden. Just as a chef selects the perfect ingredients for an ideal dish, you must choose seeds that match your garden’s climate, soil, and requirements.
Heirloom, hybrid, open-pollinated, and GMO seeds offer distinctive advantages, and understanding these categories of vegetable seeds will help you make an informed decision. As a result, you can achieve a plentiful harvest with minimal effort and more remarkable success.
Are you ready to start planting suitable vegetables or vegetable seeds? Explore expert advice and varieties today!
FAQs ❓
Check out these frequently asked questions to learn more about different types of vegetable seeds.
The primary types are heirloom, hybrid, open-pollinated, and GMO seeds, each with unique characteristics, benefits, and limitations.
Yes, heirloom seeds are open-pollinated and can be saved for future planting, making them ideal for preserving plant varieties.
Due to their mixed parentage, hybrid seeds may not produce true-to-type plants in the following generation, resulting in inconsistent traits.
Generally, no. GMO seeds are primarily used in commercial agriculture and are not typically available for home gardeners due to patent restrictions.
Cool-season seeds thrive in cooler temperatures (e.g., lettuce, peas), while warm-season seeds need warmer conditions to grow (e.g., tomatoes, peppers).

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks



- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks