What is Seed Cotyledon? The Key to Early Plant Growth
Published: 17 Dec 2025
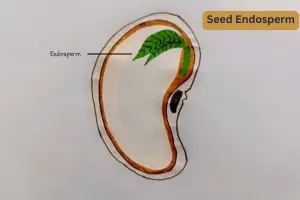
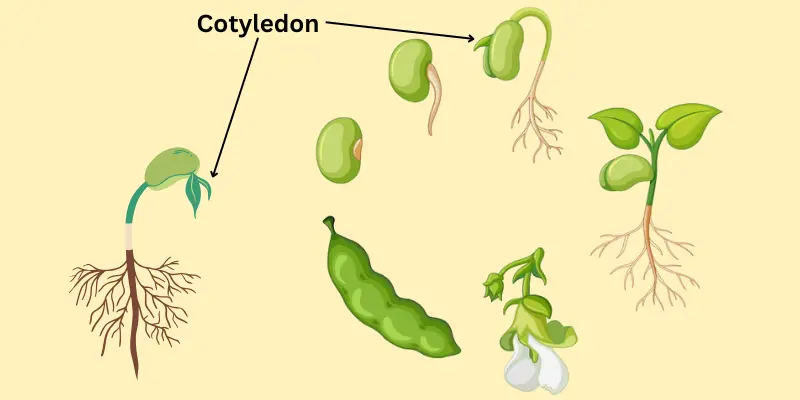
What is seed cotyledon, and why is it called a seed’s first leaf? The answer lies in its remarkable role in nourishing young plants. A seed cotyledon, often called a ‘seed leaf,’ plays a vital role in a plant’s early development. It stores nutrients to fuel the embryo’s growth and may even aid in photosynthesis in some species. Whether it’s a monocot like wheat or a dicot like beans, cotyledons are the unsung heroes of seed anatomy.
I’m Sheila, and I’ve spent over seven years exploring the amazing world of botany. Plants have always fascinated me, especially the hidden wonders inside seeds. In this article, I’ll share what I’ve learned about seed cotyledons—their types, their role in plant growth, and their importance.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand how cotyledons contribute to plant growth and why they matter. Let’s explore this together, clearly and excitingly!
Understanding: What is Seed Cotyledon?
Seed cotyledons are crucial in the early stages of a plant’s life. Think of them as the first meal a plant gets after it breaks free from its seed coat. These specialized structures nourish the young plant until it can produce its food through photosynthesis.
The creation of a thousand forests is in one acorn.Ralph Waldo Emerson
Let’s explore their definitions and the different types of cotyledons in the plant world.
Definition of Cotyledons
- Cotyledons are the first leaves that emerge when a seed starts to germinate. They play a crucial role in seed anatomy by supplying the early energy required for the plant’s growth. You can think of them as the plant’s first source of nourishment, supporting its development until it can produce food independently.
- As a botanist, I’ve seen how essential cotyledons are in ensuring healthy seedling growth, especially in the early days of germination. They differ from other seed parts, such as the seed coat and embryo, in that they play a primary role in nutrition rather than in protection or reproduction.
Types of Cotyledons
There are two main types of cotyledons based on the plant’s classification:
- Monocotyledons
- Dicotyledons
- Monocotyledons: These seeds have only one cotyledon. Some examples include grains like maize and wheat. Imagine the cotyledon as a single, influential fuel tank that provides the energy needed to kick-start the plant’s growth.
- Dicotyledons: These seeds come with two cotyledons. Beans and peas are great examples. The cotyledons serve as two storage units in these seeds, providing extra nourishment for the developing plant.
In every walk with nature, one receives far more than he seeks.John Muir
Functions of Cotyledons
Cotyledons aren’t just pretty little leaves—they are vital in helping the seedling survive and grow. They act as food storage units and energy providers for the plant in its early stages.
Let’s learn how cotyledons support a plant’s development through nutritional supply and, in some cases, photosynthesis.
Nutritional Storage and Supply
- Cotyledons store nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to nourish the developing embryo.
- They act like a pantry for the seed, providing energy until the plant can produce its food.
- Examples: Beans, peas, and other legumes are common seeds where cotyledons are storage organs.
Role in Photosynthesis
In certain plants, cotyledons contribute to early photosynthesis immediately after germination. Whether cotyledons can photosynthesise depends on the type of germination:
- Epigeal Germination: Cotyledons emerge above the soil and start photosynthesising (e.g., beans).
- Hypogeal Germination: Cotyledons remain below the soil surface and do not use photosynthesis (e.g., peas).
Personal Experience
- The ability of cotyledons to either perform photosynthesis or stay underground plays a key role in determining the speed and success of plant growth.

Structure of Cotyledons in Seeds
The structure of cotyledons is as fascinating as it is essential for seedling growth. Cotyledons not only differ in their appearance but also in how they function depending on the plant type.
Let’s discuss their composition and structure and how they relate to other seed parts.
Anatomical Features
Cotyledons are made up of tissues that store nutrients to fuel the developing embryo. They can be thick and fleshy, as in dicots, or thin and leaf-like, as in monocots. Think of them as the “first aid kit” for a plant, offering all the nourishment it needs to grow strong.
- Monocots: These seeds have a single, strap-like cotyledon (e.g., corn, wheat). The cotyledon is usually narrow and doesn’t look much like a typical leaf.
- Dicots: These seeds have two cotyledons (e.g., beans and sunflowers). The cotyledons are broader and often resemble the plant’s first leaves.

Relationship with Other Seed Parts
- Cotyledons are closely connected to other key parts of the seed, including the seed coat and the embryo. They act as the interface between the seed’s protective outer layer and the growing plant. Cotyledons are the bridge, helping transfer nutrients from the seed coat to the embryo.
- In my research, I’ve noticed how cotyledons often work hand-in-hand with the seed coat to provide the embryo with everything it needs to germinate and sprout. The integration between these parts is essential for healthy seedling development.
| Trivia facts about cotyledon |
|---|
|
Significance of Cotyledons in Plant Growth
Cotyledons play an irreplaceable role in the early stages of plant development. Think of them as the power-up a plant needs to begin its journey to maturity. From the moment a seed sprouts, cotyledons provide essential nutrients and energy that set the foundation for healthy growth.

Let’s explore why they’re so crucial for germination and seedling development.
Importance in Germination and Seedling Development
- Cotyledons are a plant’s first leaves, storing essential nutrients in the seed.
- They offer the energy needed for early growth until the plant can start photosynthesising.
- Without cotyledons, plants would struggle to establish themselves during germination.
- My experience with plant embryos shows how cotyledons directly impact the speed and strength of seedling growth, ensuring they’re prepared to grow above ground.
To plant a garden is to believe in tomorrow.Audrey Hepburn
Conclusion
So, guys, it’s time to wrap up. In this article, we’ve covered what a seed cotyledon is in detail as someone who has studied these fascinating structures.
I recommend paying close attention to the cotyledons in your seeds, as they provide vital nutrients and play a massive role in the plant’s early development.
I encourage you to keep learning and experimenting with your gardening. Want more expert advice? Explore our other articles and stay connected for more valuable insights!
Frequently Asked Questions
These FAQs provide clear, beginner-friendly guidance to help readers better understand cotyledon:
A cotyledon is a leaf-like structure in a seed that stores nutrients to help the plant grow. It provides the energy needed for the seed to sprout and start developing. Depending on the plant, a seed may have one or two cotyledons.
Cotyledons are crucial for early plant growth because they store nutrients. These nutrients help the plant survive before it can start photosynthesising. Without cotyledons, the plant would struggle to grow and establish itself.
After germination, cotyledons either remain in the soil or rise above it. They may stay underground in some plants (hypogeal germination) or be pushed above the soil (epigeal germination) to help with early photosynthesis. In either case, they provide initial nourishment to the plant.
Yes, all plants with seeds have cotyledons. Cotyledons are essential in their early growth, whether the plant is a tree, flower, or grass. However, the number and structure can vary between species.
Yes, cotyledons are not true leaves. True leaves appear after the cotyledons and are responsible for long-term photosynthesis. Cotyledons are temporary and mainly serve as energy sources for the growing plant.
Yes, the number and structure of cotyledons can help identify whether a plant is a monocot or a dicot. Botanists often use this feature to classify plants, as it’s a key characteristic of their early growth. By observing the cotyledons, you can get clues about the plant’s species.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks